- Qingqingquan
- Shandong, China
- 20 days
- 300 units per month
This article systematically introduces the core technologies in the current water treatment field, analyzes its technical principles, application scenarios and future development trends
Core technologies of modern water treatment: water quality revolution driven by innovation(Ⅰ)
As the global water shortage problem becomes increasingly severe, water treatment technology is undergoing unprecedented changes and innovations. This article will systematically introduce the core technologies in the current water treatment field, analyze its technical principles, application scenarios and future development trends.
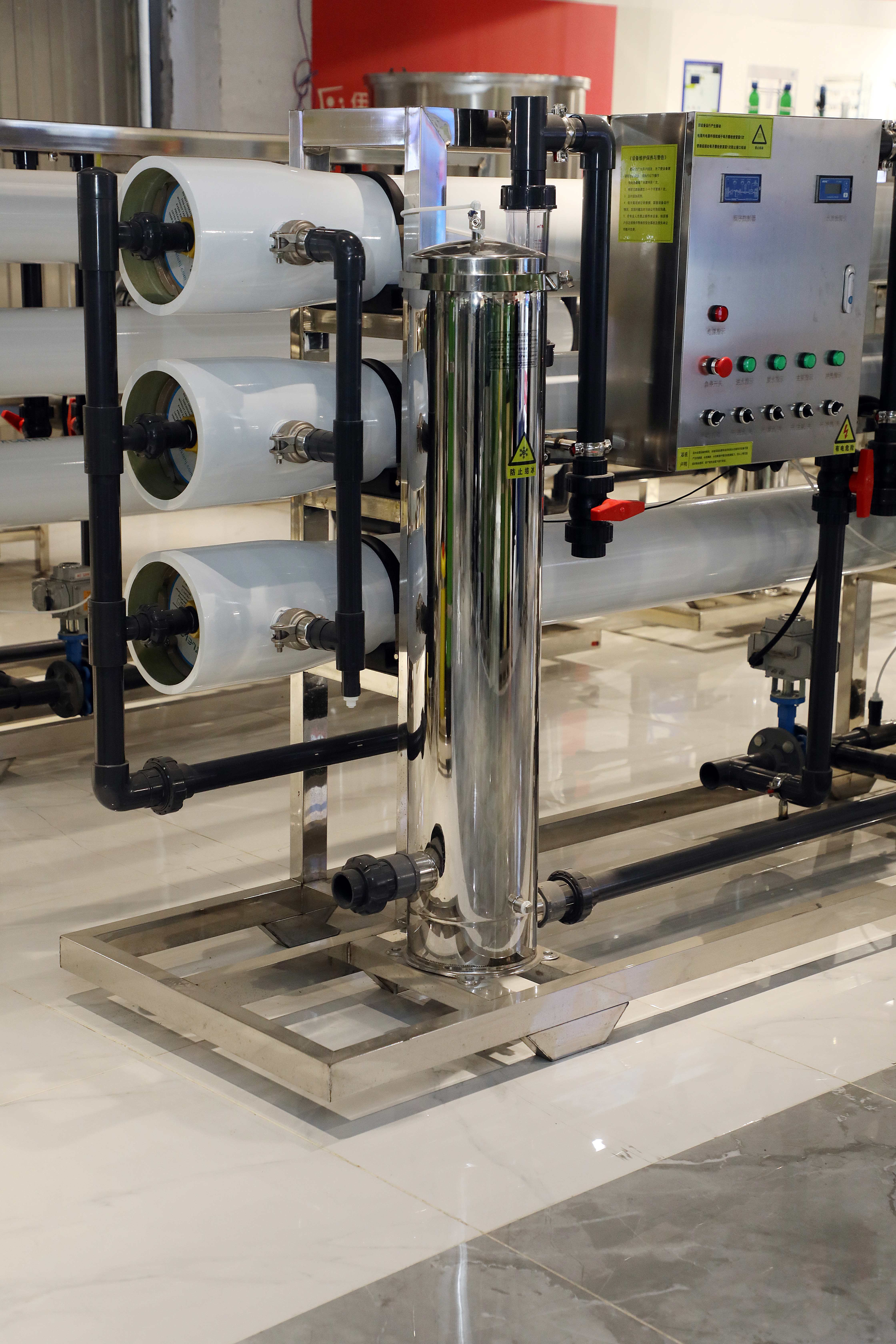
1. Membrane separation technology: the mainstay of water treatment
1.1 Reverse osmosis technology
Technical principle: using the selective permeability of semipermeable membranes to achieve separation of solvents and solutes under external pressure
Application advantages: desalination rate is as high as 95%, which can effectively remove pollutants such as soluble salts and heavy metals
Typical applications: seawater desalination, ultrapure water preparation, industrial wastewater treatment
1.2 Nanofiltration technology
Technical features: between ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis, with selective separation characteristics
Unique advantages: can retain some beneficial minerals while effectively removing harmful substances
Main applications: deep treatment of drinking water, industrial separation process
1.3 Research and development of new membrane materials
Graphene membrane: with atomic-level thickness and ultra-high permeability
Bionic membrane: imitate Selective permeation mechanism of biofilm
Intelligent response membrane: separation performance can be adjusted with environmental conditions

2. Advanced oxidation technology: the nemesis of difficult-to-degrade pollutants
2.1 Ozone oxidation technology
Reaction mechanism: direct decomposition of organic matter through strong oxidizing properties
Technical advantages: fast reaction speed and no secondary pollution
Application areas: drinking water disinfection, industrial wastewater treatment
2.2 Photocatalytic oxidation technology
Working principle: using light energy to excite catalysts to produce strong oxidizing free radicals
Technical features: mild reaction conditions and thorough degradation
Typical applications: micro-polluted water treatment, VOCs degradation
2.3 Electrochemical oxidation technology
Core advantages: no need to add chemical agents, strong reaction controllability
Innovation direction: research and development of efficient electrode materials, reactor optimization design










































